nginx Webserver - Installation, Configuration, Operations
Installation
Debian 12
See Installation instructions: Debian:
“Before you install nginx for the first time on a new machine, you need to set up the nginx packages repository. Afterward, you can install and update nginx from the repository.”
Install the prerequisites:
$ sudo apt install curl gnupg2 ca-certificates lsb-release debian-archive-keyring
Import an official nginx signing key so apt could verify the packages authenticity. Fetch the key:
$ curl https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key | gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/nginx-archive-keyring.gpg > /dev/null
Verify that the downloaded file contains the proper key:
$ gpg --dry-run --quiet --no-keyring --import --import-options import-show /usr/share/keyrings/nginx-archive-keyring.gpg
pub rsa4096 2024-05-29 [SC]
8540A6F18833A80E9C1653A42FD21310B49F6B46
uid nginx signing key <signing-key-2@nginx.com>
pub rsa2048 2011-08-19 [SC] [expires: 2027-05-24]
573BFD6B3D8FBC641079A6ABABF5BD827BD9BF62
uid nginx signing key <signing-key@nginx.com>
pub rsa4096 2024-05-29 [SC]
9E9BE90EACBCDE69FE9B204CBCDCD8A38D88A2B3
uid nginx signing key <signing-key-3@nginx.com>
The output should contain the full fingerprint 573BFD6B3D8FBC641079A6ABABF5BD827BD9BF62 as follows:
pub rsa2048 2011-08-19 [SC] [expires: 2027-05-24]
573BFD6B3D8FBC641079A6ABABF5BD827BD9BF62
uid nginx signing key <signing-key@nginx.com>
Note that the output can contain other keys used to sign the packages.
To set up the apt repository for stable nginx packages, run the following command:
$ echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/nginx-archive-keyring.gpg] \
http://nginx.org/packages/debian `lsb_release -cs` nginx" \
| sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nginx.list
deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/nginx-archive-keyring.gpg] http://nginx.org/packages/debian bookworm nginx
Set up repository pinning to prefer our packages over distribution-provided ones:
$ echo -e "Package: *\nPin: origin nginx.org\nPin: release o=nginx\nPin-Priority: 900\n" \
| sudo tee /etc/apt/preferences.d/99nginx
Package: *
Pin: origin nginx.org
Pin: release o=nginx
Pin-Priority: 900
To install nginx, run the following commands:
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt install nginx
...
The following NEW packages will be installed:
logrotate nginx
...
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Thanks for using nginx!
Please find the official documentation for nginx here:
* https://nginx.org/en/docs/
Please subscribe to nginx-announce mailing list to get
the most important news about nginx:
* https://nginx.org/en/support.html
Commercial subscriptions for nginx are available on:
* https://nginx.com/products/
----------------------------------------------------------------------
...
Setting up nginx (1.26.3-1~bookworm) ...
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/nginx.service → /lib/systemd/system/nginx.service.
...
Configuration
Entry point /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
The entry file for configuration of nginx is /etc/nginx/nginx.conf:
user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log notice;
pid /var/run/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
}
It includes all conf-files from directory /etc/nginx/conf.d/.
Default configuration /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
The default-configuration is /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf:
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#access_log /var/log/nginx/host.access.log main;
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
To list only the active lines:
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
}
}
Default webpages
The webpages of the default configuration can be found under /usr/share/nginx/html:
$ ls -al /usr/share/nginx/html
total 16
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Mar 2 13:37 .
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Mar 2 13:37 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 497 Feb 5 11:07 50x.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 615 Feb 5 11:07 index.html
Domain A-Record
For serving webpages for a domain, the DNS-A-Record (“Address record”) for the domain has to be configured to the IP-address of your server (see Wikipedia):
“Returns a 32-bit IPv4 address, most commonly used to map hostnames to an IP address of the host.”
This often can be done in the administration area of your hosting company.
Virtual Hosts
nginx is able to serve several domains (“virtual hosts”) with one installation.
Serving a website
For each virtual host we create an own directory under /var/www and an own configuration file under /etc/nginx/conf.d/.
Let’s create a virtual host for “www.munhattan.com”:
Create directories for static files:
$ sudo mkdir -p /var/www/www.munhattan.com/htdocs
$ sudo mkdir -p /var/www/www.munhattan.com/logs
$ sudo chown -R nginx:nginx /var/www/www.munhattan.com
Create a basic webpage:
$ sudo nano /var/www/www.munhattan.com/htdocs/index.html
<html>
<body>
<center>
<h1>www.munhattan.com</h1>
<small><i>provided by datazuul.com</i></small>
</center>
</body>
</html>
$ sudo chown -R nginx:nginx /var/www/www.munhattan.com
Create configuration file:
$ cd /etc/nginx/conf.d/
$ sudo cp default.conf www.munhattan.com.conf
Edit configuration:
$ sudo nano www.munhattan.com.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.munhattan.com munhattan.com;
access_log /var/www/www.munhattan.com/logs/access.log main;
location / {
root /var/www/www.munhattan.com/htdocs;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
}
}
Reload nginx:
$ sudo systemctl reload nginx
The webpage should now be reachable under http://www.munhattan.com.
Serving as proxy server to underlying service
If you want to create a virtual host for proxying requests to an underlying service (like a Spring Boot application) with a different port (e.g. 10000), we do not need directories for static content, just the configuration file and a directory for the logs.
Example for api.your_host.com:
Create directory for logs:
$ sudo mkdir -p /var/www/api.your_host.com/logs
$ sudo chown -R nginx:nginx /var/www/api.your_host.com
Create configuration file:
$ cd /etc/nginx/conf.d/
$ sudo cp default.conf api.your_host.com.conf
Edit configuration:
$ sudo nano api.your_host.com.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name api.your_host.com;
access_log /var/www/api.your_host.com/logs/access.log main;
#location / {
# root /usr/share/nginx/html;
# index index.html index.htm;
#}
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:10000/;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
}
}
Reload nginx:
$ sudo systemctl reload nginx
The API should now be reachable under http://api.your_host.com.
Operations
Show status of nginx
When not started, yet:
$ systemctl status nginx
○ nginx.service - nginx - high performance web server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; enabled; preset: enabled)
Active: inactive (dead)
Docs: https://nginx.org/en/docs/
Start nginx
$ sudo systemctl start nginx
$ systemctl status nginx
● nginx.service - nginx - high performance web server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; enabled; preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Sun 2025-03-02 14:12:42 UTC; 46s ago
Docs: https://nginx.org/en/docs/
Process: 3522 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/nginx -c ${CONFFILE} (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 3523 (nginx)
Tasks: 7 (limit: 19105)
Memory: 5.7M
CPU: 12ms
CGroup: /system.slice/nginx.service
├─3523 "nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf"
├─3524 "nginx: worker process"
├─3525 "nginx: worker process"
├─3526 "nginx: worker process"
├─3527 "nginx: worker process"
├─3528 "nginx: worker process"
└─3529 "nginx: worker process"
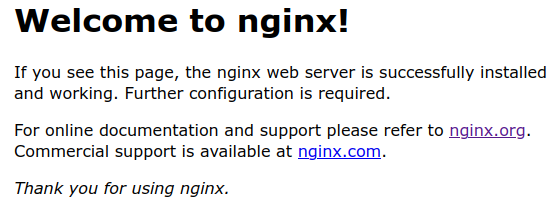
Test it by calling http://your_domain/. You will see the default webpage:
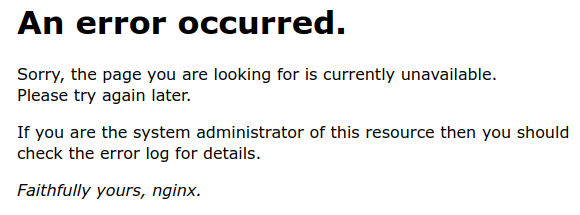
The server error page can be viewed requesting htpp://your_domain/50x.html: